|
Demansia vestigiata
|
|
Family: Elapidae
|
|
Subfamily: Elapinae
|
|
Genus: Demansia
|
|
Species: vestigiata
|
Common Names
Black Whip Snake , Lesser Black Whip Snake
|
Region
Australia + New Guinea + Indonesia
|
Countries
Australia, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea
|
|
|
|
|
|
Taxonomy and Biology
|
|
Adult Length: 1.00 m
|
General Shape
Large in length, whip-like in appearance, slender bodied snake with a long tail. Can grow to a maximum of about 1.78 metres. Head is deep, barely distinct from neck with a sharp canthus rostralis. Snout is rounded when viewed from above. Eyes are large in size with round pupils. Dorsal scales are smooth, 15 scale rows at midbody with reduction to 13 scale rows well before the cloaca.
|
Habitat
Warm temperate to tropical slopes and plains with dry open forest or woodland, often in drier areas with a well grassed understorey.
|
Habits
Diurnal and terrestrial snake with a nocturnal tendency in very hot and humid weather. A particularly swift moving predator which forages for, and pursues its prey. Nervous disposition, prefers to escape if confronted and reluctant to bite even when cornered and provoked. Often found sheltering under logs, flat rocks, rock crevices, cracks in parched soil, rabbit burrows, in dense vegetation or leaf litter.
|
Prey
Feeds mainly on lizards ( particularly skinks and agamids ) and frogs when available.
|
|
|
|
Venom
|
General: Venom Neurotoxins
Unknown
|
General: Venom Myotoxins
Unknown
|
General: Venom Procoagulants
Unknown
|
General: Venom Anticoagulants
Unknown
|
General: Venom Haemorrhagins
Unknown
|
General: Venom Nephrotoxins
Unknown
|
General: Venom Cardiotoxins
Unknown
|
General: Venom Necrotoxins
Unknown
|
General: Venom Other
Unknown
|
|
|
|
Clinical Effects
|
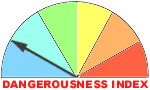
General: Dangerousness
Moderate envenoming possible but unlikely to prove lethal
|
|
General: Rate of Envenoming: Unknown but likely to be low
|
|
General: Untreated Lethality Rate: Unlikely to prove lethal
|
General: Local Effects
Local pain & swelling
|
General: Local Necrosis
Not likely to occur
|
General: General Systemic Effects
Insufficient clinical reports to know
|
General: Neurotoxic Paralysis
Does not occur, based on current clinical evidence
|
General: Myotoxicity
Does not occur, based on current clinical evidence
|
General: Coagulopathy & Haemorrhages
Does not occur, based on current clinical evidence
|
General: Renal Damage
Does not occur, based on current clinical evidence
|
General: Cardiotoxicity
Does not occur, based on current clinical evidence
|
General: Other
Insufficient clinical reports to know
|
|
|
|
First Aid
|
|
Description: First aid for bites by Elapid snakes which do not cause significant injury at the bite site (see Comments for partial listing), but which may have the potential to cause significant general (systemic) effects, such as paralysis, muscle damage, or bleeding.
|
Details
1. After ensuring the patient and onlookers have moved out of range of further strikes by the snake, the bitten person should be reassured and persuaded to lie down and remain still. Many will be terrified, fearing sudden death and, in this mood, they may behave irrationally or even hysterically. The basis for reassurance is the fact that many venomous bites do not result in envenoming, the relatively slow progression to severe envenoming (hours following elapid bites, days following viper bites) and the effectiveness of modern medical treatment.
2. The bite wound should not be tampered with in any way. Wiping it once with a damp cloth to remove surface venom is unlikely to do much harm (or good) but the wound must not be massaged. For Australian snakes only, do not wash or clean the wound in any way, as this may interfere with later venom detection once in a hospital.
3. All rings or other jewellery on the bitten limb, especially on fingers, should be removed, as they may act as tourniquets if oedema develops.
4. If the bite is on a limb, a broad bandage (even torn strips of clothing or pantyhose) should be applied over the bitten area at moderate pressure (as for a sprain; not so tight circulation is impaired), then extended to cover as much of the bitten limb as possible, including fingers or toes, going over the top of clothing rather than risking excessive limb movement by removing clothing. The bitten limb should then be immobilised as effectively as possible using an extemporised splint or sling.
5. If there is any impairment of vital functions, such as problems with respiration, airway, circulation, heart function, these must be supported as a priority. In particular, for bites causing flaccid paralysis, including respiratory paralysis, both airway and respiration may be impaired, requiring urgent and prolonged treatment, which may include the mouth to mask (mouth to mouth) technique of expired air transfer. Seek urgent medical attention.
6. Do not use Tourniquets, cut, suck or scarify the wound or apply chemicals or electric shock.
7. Avoid peroral intake, absolutely no alcohol. No sedatives outside hospital. If there will be considerable delay before reaching medical aid, measured in several hours to days, then give clear fluids by mouth to prevent dehydration.
8. If the offending snake has been killed it should be brought with the patient for identification (only relevant in areas where there are more than one naturally occurring venomous snake species), but be careful to avoid touching the head, as even a dead snake can envenom. No attempt should be made to pursue the snake into the undergrowth as this will risk further bites.
9. The snakebite victim should be transported as quickly and as passively as possible to the nearest place where they can be seen by a medically-trained person (health station, dispensary, clinic or hospital). The bitten limb must not be exercised as muscular contraction will promote systemic absorption of venom. If no motor vehicle or boat is available, the patient can be carried on a stretcher or hurdle, on the pillion or crossbar of a bicycle or on someone's back.
10. Most traditional, and many of the more recently fashionable, first aid measures are useless and potentially dangerous. These include local cauterization, incision, excision, amputation, suction by mouth, vacuum pump or syringe, combined incision and suction ("venom-ex" apparatus), injection or instillation of compounds such as potassium permanganate, phenol (carbolic soap) and trypsin, application of electric shocks or ice (cryotherapy), use of traditional herbal, folk and other remedies including the ingestion of emetic plant products and parts of the snake, multiple incisions, tattooing and so on.
|
|
|
|
Treatment
|
Treatment Summary
Major envenoming unlikely, but assess fully and observe for at least 12 hrs. No specific antivenom available.
|
Key Diagnostic Features
Local pain & swelling, possibly general systemic symptoms
|
General Approach to Management
It is possible that most cases will be minor, but some cases may be more severe, requiring admission and treatment, so assess carefully before discharge.
|
Antivenom Therapy
No antivenom available
|
|
|
|
Images
|
|
No images for Images
|
|
|



